While Facebook and Twitter host a broad range of user activities, a study asked, what does off-label use look like on an app like Tinder, which has an articulated label? Further, how does off-label use play out when other users expect that the app has fixed purposes?
Search Results: Phishing (91)
The brutal war in Yemen may appear like any traditional regional conflict with guns on the ground, but it is…
These days, it’s hard to know whom to trust online, and how to discern genuine content from fakery. Some degree of trust…
Ransomware usually spreads via phishing emails or links to infected websites, relying on human error to gain access to systems. As its name suggests, ransomware is designed to block access to data, systems or services until a ransom is paid. At a technical level, cities tend to be fairly easy targets because they often have bespoke operating systems, with parts that are old and out-of-date, as well as ineffective back-up measures.
The new version of Apple’s macOS, that’ll be available for free download come our spring time, is called macOS Catalina. And this is what you need to know about it.
Research has shown that when computers were fitted with proximity sensors (which facilitate online security by automatically logging users out when they move away from the machine) users began placing cups over the sensors to disable them.
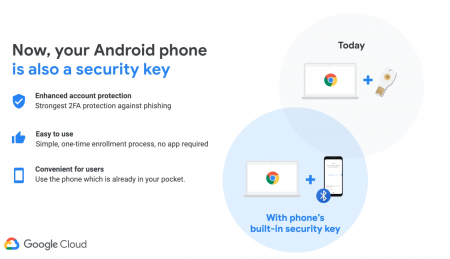
These days you can’t be too safe with data phishing attacks, and now a developer has found that even Chrome for Android is susceptible.
Two-factor authentication is a service that keeps your online accounts and services a whole lot safer than they would be otherwise. Why else would you lock down a Steam account using Steam Guard, a Blizzard account with Blizzard Authenticator, an Xbox Live account with whichever notification system from Microsoft annoys you the least? Shouldn’t your more business-y accounts have the same protection? Google thinks so.
Once a piece of ransomware has got hold of your valuable information, there is very little you can do to get it back other than accede to the attacker’s demands. Ransomware, a type of malware that holds a computer to ransom, has become particularly prevalent in the past few years and virtually unbreakable encryption has made it an even more powerful force.
Every day, often multiple times a day, you are invited to click on links sent to you by brands, politicians, friends and strangers. You download apps on your devices. Maybe you use QR codes.
Most of these activities are secure because they come from sources that can be trusted. But sometimes criminals impersonate trustworthy sources to get you to click on a link (or download an app) that contains malware.