The restrictions associated with the COVID-19 pandemic drove life online in 2020, where it will probably remain for much of 2021. The…
Browsing: The Conversation
Bitcoin continues to trade close to its all-time high reached this month. Its price recently reached around US $34,000 — up…
What is the cost of propaganda, misinformation and conspiracy theories? Democracy and public safety, to name just two things. The…
Spotify offered the promise that, in the age of digital downloads, all artists would get paid for their music, and…
Space exploration achieved several notable firsts in 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic, including commercial human spaceflight and returning samples of an asteroid to Earth.…
In Lewis Carroll’s Victorian classic Through the Looking-Glass, Alice steps through a mirror into a world that is a reflection of…
Have you been hitting the gym again with COVID restrictions easing? Or getting back into running, cycling, or playing team…
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it clearer than ever that we are at risk of losing control of our economies. Our…
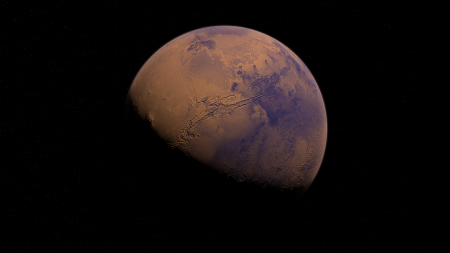
NASA is planning to land a crew on the Moon by 2024, and then onward to Mars, possibly in the 2030s. One…
Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s own words play a starring role in the government’s case to break up his social network. “It…