In February this year, reports surfaced on Twitter and Facebook that the Ukrainian government was undertaking a mass genocide of civilians. Around the same time, conspiracy theorists began saying Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy was an agent of the “New World Order”.
These claims have been thoroughly debunked, but not before attracting millions of views and offering a purported justification for Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. More recently, Russian and Chinese officials have claimed the United States has funded bioweapons research in Ukraine.
Social media has played a crucial role in the spread of these and other false claims. We have identified a network of dozens of Russian government Twitter accounts using a loophole in the platform’s rules to run a coordinated program of disinformation.
The dangers of disinformation
By “disinformation”, we mean factually incorrect material distributed with the aim of unsettling or damaging something or someone: a politician, a political party or system, or a way of life.
Since the 2016 US elections, disinformation has been recognised as a growing threat to democracy.
Democracy relies on citizens’ ability to make informed decisions about policy, politics and world affairs. This ability is severely compromised when fake and (deliberately) misleading claims are promoted as fact.
As we have seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, disinformation can also pose a grave threat to public health and safety.
Disinformation itself is not new, but over the past decade it has found an ideal place to flourish on social media platforms.
Why disinformation loves social media
Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and many other platforms are designed as amplification systems. They are built to be open to all comers and increase the volume on any type of content.
Anyone with an internet connection can access social media, where all kinds of content can be shared with a speed and reach that was impossible with heritage media.
The sheer speed at which disinformation is disseminated – especially via automated “bot accounts” – makes it hard for content moderators to keep up. The emotive, partisan nature of much online disinformation also means internet users and journalists are more likely to spread it without checking it too closely.
Russian accounts on Twitter
Russian government Twitter accounts have played a key role in the spread of pro-Russia disinformation. While Twitter has fewer users than Facebook or Instagram, it is a pivotal site for the production and dissemination of news.
We tracked the Twitter activity of 75 official Russian government accounts and found they are a major source and amplifier of disinformation. At time of writing these accounts together have a total of 7,366,622 followers. They have been retweeted 35.9 million times, received 29.8 million likes, and 4 million replies.
Between 25 February and 3 March 2022, about these accounts made 1,157 tweets – and around three quarters were about Ukraine. The accounts have tried to spread false narratives to justify the invasion.
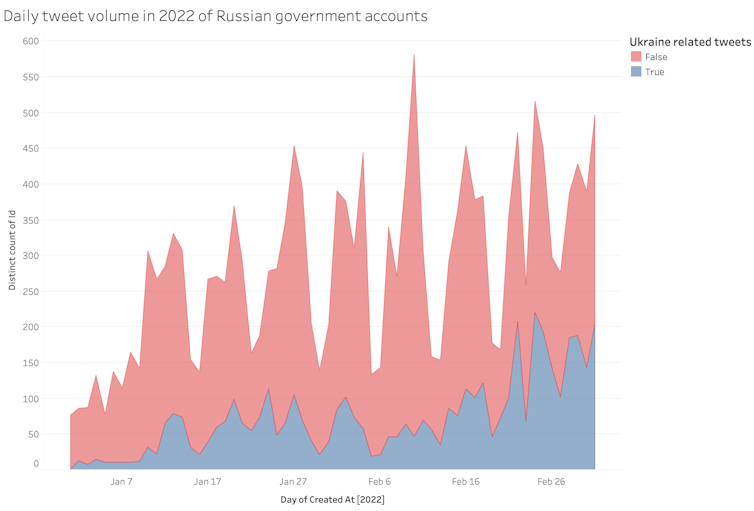
The tweets below show Russian government accounts spreading disinformation narratives: delegitimising Ukraine as a sovereign state, sowing doubt and mistruths about the Ukraine government and neo-Nazi infiltration, spreading “whataboutisms” that downplay the Ukraine invasion by drawing attention to alleged war crimes by other countries, and spreading conspiracy theories about Ukraine/US bioweapons research.
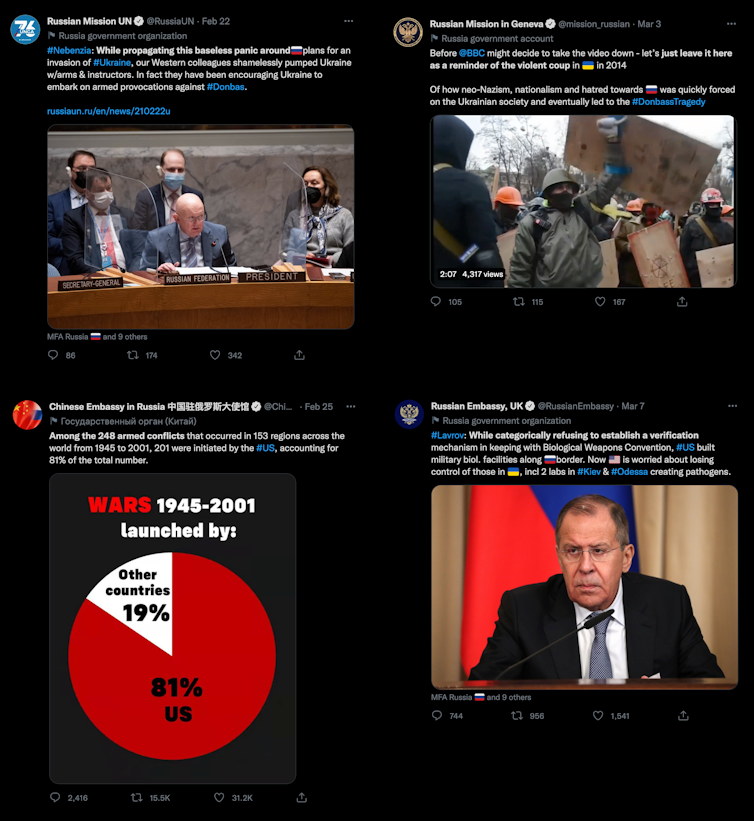
A loophole for governments
Twitter has recognised the disinformation possibilities of state-affiliated media, putting warning labels on their content and not recommending or amplifying them.
However, these rules do not apply to government-controlled accounts not labelled as media, such as foreign embassies.
As a result, these accounts are flooding the platform with propaganda. This is a critical gap in Twitter’s moderation practices, and one that has received little attention.
A coordinated network
The 75 Russian government accounts we studied are also working together to amplify disinformation. We analysed their tweets and found they often retweet the same content at about the same time.
This is a well-known tactic of coordinated disinformation or “astroturfing”, where a network of accounts retweet content together repeatedly to amplify it and maximise its reach.
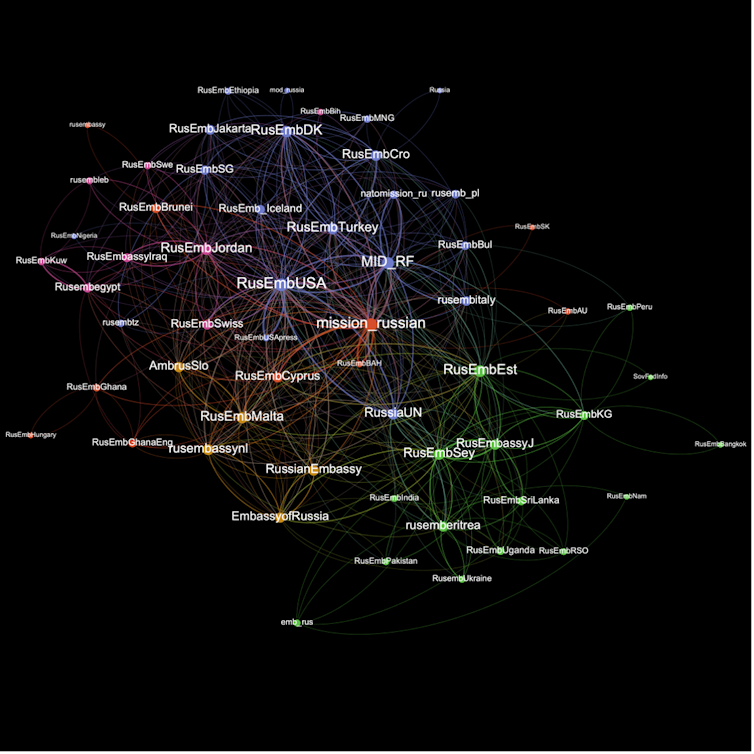
The picture above shows a network visualisation of coordinated retweet behaviour among the 75 Russian government accounts. Larger nodes coordinate more often, links indicate retweeting within 60 seconds of one another, and the colours represent “communities” of accounts that tend to co-retweet especially frequently.
The most prominent accounts re the two Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs accounts (@mfa_russia and @mid_rf), the Russian Mission in Geneva (@mission_russian), and the Russian Embassy in USA (@rusembusa).
What can be done?
Twitter needs to do more to safeguard the platform from harmful content by state actors. Government accounts are still free to flood the space with false information.
Twitter’s policies and rules need to be modified to suit special circumstances such as war. They also need to adapt to non-Western contexts where disinformation is easily missed by automated moderation tuned to the English language and the norms of the US and western Europe.
Platforms have traditionally taken their cues from the techno-libertarian adage that “information wants to be free”. This has turned out to be a disaster for liberal democracy and public health.
Some positive changes have been made, particularly after the January 6 Capitol riots in the US, but platforms are still designed on the principle that the other side should always be heard.
This design is not simply the result of an impoverished understanding of political theory by young white male Silicon Valley entrepreneurs. It’s good for business: blocking government disinformation could result in governments blocking platforms in retaliation, cutting off valuable users.
Do your homework
Individual Twitter users can also help stem the spread of state-issued disinformation by doing exactly what conspiracists and disinformation actors have long encouraged: their own research.
Users can and should ask themselves: How accurate is this claim? How can the claim be verified? Who is posting this information about Russia? What stake does that person or persons have in Russian state affairs? How might amplifying this content, even to criticise it, unwittingly spread it further?
If a piece of information cannot be verified, or appears to be driven by bias or prejudice, it is in everyone’s best interest not to tweet or retweet.
- is a Senior Lecturer, Queensland University of Technology
- is a Lecturer (Early Career Development Fellow) and Program Manager, Professional Communication program, RMIT University
This article first appeared in The Conversation.




